Empathy Map
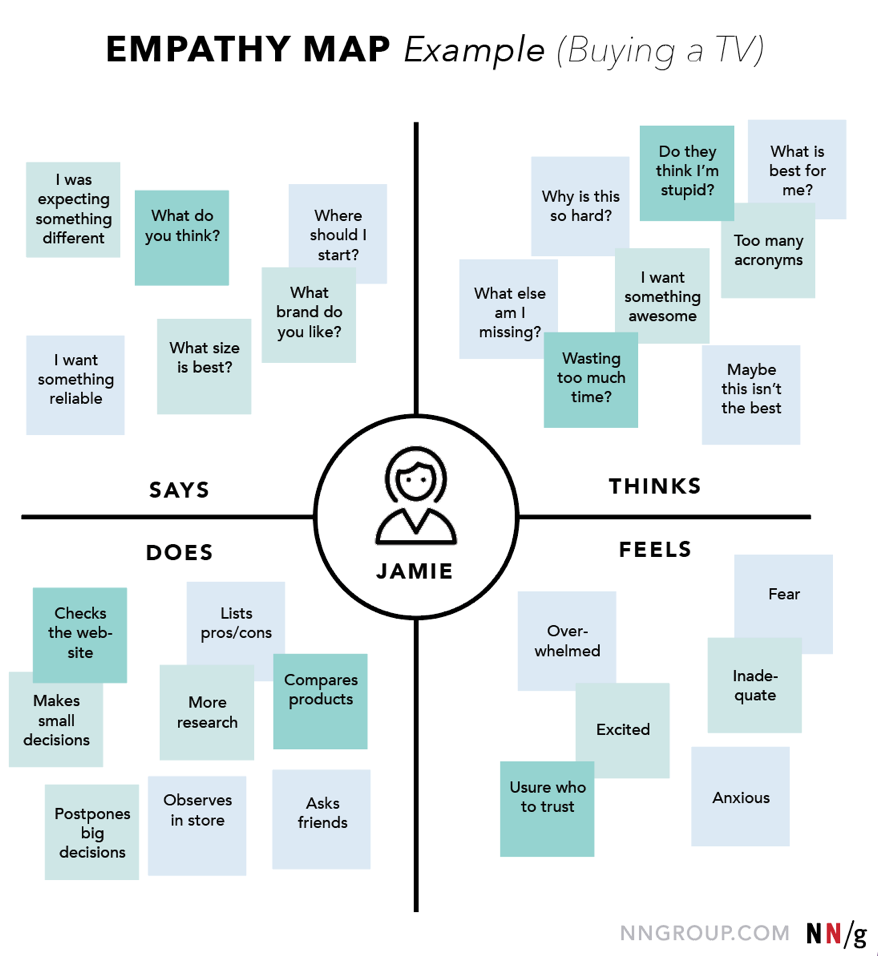
In the realm of design thinking and user-centered methodologies, empathy mapping stands out as a potent tool for understanding the intricacies of human experiences. Whether you’re crafting a product, service, or solution, the ability to empathize with your users is paramount. Empathy mapping serves as a structured approach to delve into the thoughts, feelings, and motivations of individuals, thereby enabling designers, marketers, and innovators to create more meaningful and impactful experiences.
Understanding Empathy Mapping:
Empathy mapping is a visualization technique that helps teams gain deeper insights into their target audience’s perspectives. It involves creating a visual representation of a persona’s emotions, behaviors, aspirations, and pain points. This tool facilitates empathy by encouraging stakeholders to step into the shoes of their users and view the world through their eyes.
Components of an Empathy Map:
- Senses: This section focuses on what the persona sees, hears, says, and does. It provides insights into their immediate environment, including their interactions with others and their verbal and non-verbal communication cues.
- Feelings: Understanding the emotions experienced by the persona is crucial for empathetic design. This segment captures their fears, desires, frustrations, and aspirations, shedding light on their underlying motivations.
- Pain Points: Identifying the challenges and obstacles faced by the persona allows teams to pinpoint areas where improvements or solutions are needed. By empathizing with their struggles, designers can develop interventions that address genuine needs.
- Gains: This aspect explores the persona’s goals, ambitions, and perceived benefits. By recognizing what they hope to achieve or attain, teams can tailor their offerings to align with the users’ desired outcomes.
The Process of Creating an Empathy Map:
- Research and Data Collection: Empathy mapping begins with gathering information about the target audience through various research methods such as interviews, surveys, observations, and market analysis. This phase aims to collect qualitative data that provides insights into users’ behaviors, preferences, and pain points.
- Persona Development: Based on the collected data, teams create fictional personas that represent different segments of their target audience. Each persona embodies specific demographic characteristics, needs, and goals, serving as a reference point for empathy mapping exercises.
- Empathy Mapping Workshop: Teams collaborate in a workshop setting to populate the empathy map for each persona. Using sticky notes or digital tools, participants brainstorm and document observations related to the senses, feelings, pain points, and gains of the persona. This collaborative process encourages diverse perspectives and ensures a comprehensive understanding of the user’s experience.
- Analysis and Insights Generation: Once the empathy maps are populated, teams analyze the gathered information to uncover patterns, trends, and key insights. They identify common themes across different personas and prioritize areas that warrant further exploration or intervention.
- Iterative Refinement: Empathy mapping is an iterative process that evolves as teams gather more data and insights. Teams continuously refine their empathy maps based on user feedback, usability testing, and market dynamics, ensuring that their solutions remain relevant and responsive to users’ needs.
Benefits of Empathy Mapping:
- Human-Centered Design: Empathy mapping promotes a human-centered approach to problem-solving, placing the needs and experiences of users at the forefront of the design process. By empathizing with users, teams can develop solutions that resonate with their audience on a deeper level.
- Enhanced Understanding: By visualizing the user’s experience through empathy maps, teams gain a holistic understanding of their audience’s motivations, behaviors, and pain points. This comprehensive view enables more informed decision-making and solution development.
- Alignment and Collaboration: Empathy mapping workshops foster collaboration and alignment among cross-functional teams by bringing stakeholders together to co-create shared understanding. By engaging diverse perspectives, teams can generate innovative ideas and solutions that address multifaceted user needs.
- Improved Communication: Empathy maps serve as powerful communication tools, allowing teams to convey complex user insights in a concise and visually engaging format. Whether presenting to stakeholders, clients, or team members, empathy maps facilitate clearer communication and alignment around user-centric priorities.
- Iterative Improvement: Empathy mapping supports an iterative approach to design and innovation, enabling teams to continuously refine their understanding of users and iterate on their solutions based on feedback and learning. This iterative cycle fosters innovation and ensures that products and services evolve to meet changing user needs and preferences.
Conclusion:
Empathy mapping is more than just a design tool; it’s a mindset that fosters deep understanding, empathy, and collaboration. By visualizing the human experience through empathy maps, teams can uncover insights that inform the creation of more meaningful and impactful solutions. Whether designing products, services, or experiences, the power of empathy mapping lies in its ability to illuminate the path towards truly user-centered innovation. Embracing empathy as a core principle, organizations can forge stronger connections with their audience and create experiences that resonate on a profound emotional level.





