Dismissive
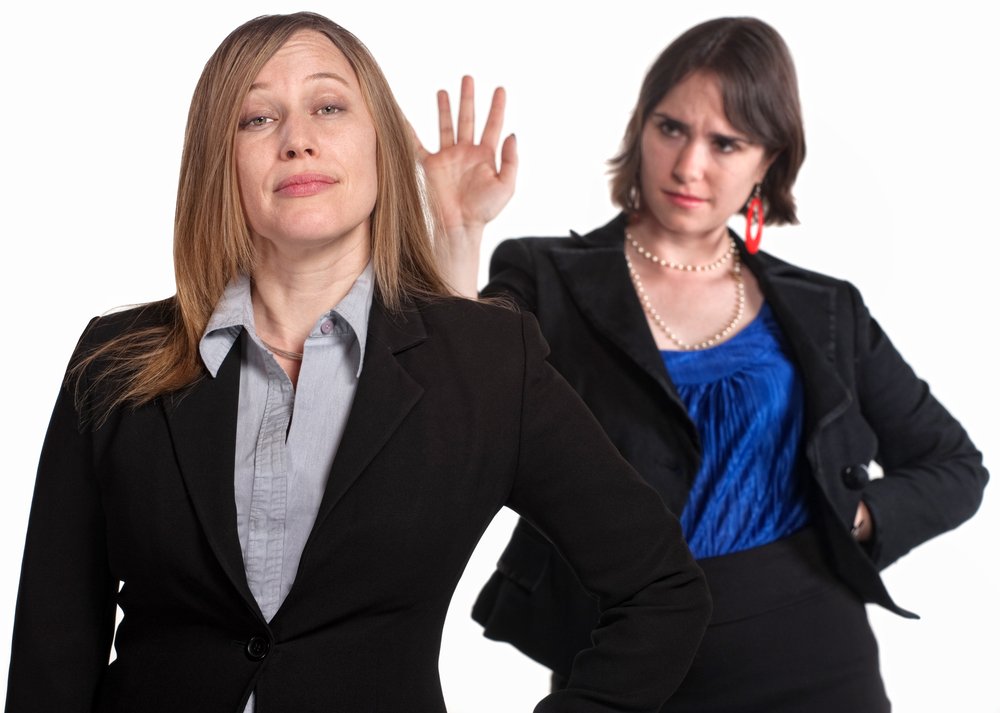

Dismissiveness, a psychological behavior marked by a tendency to minimize or disregard the thoughts, feelings, or ideas of others, is a complex phenomenon that permeates various aspects of human interaction. Whether it’s in personal relationships, professional settings, or societal dynamics, dismissiveness can breed misunderstanding, conflict, and hindered growth. In this article, we delve into the intricacies of dismissiveness, exploring its causes, effects, and strategies for overcoming it.
Table of Contents
ToggleUnderstanding Dismissiveness:
At its core, dismissiveness often stems from a combination of internal and external factors. Individuals may develop dismissive tendencies as a defense mechanism, shielding themselves from perceived threats or discomfort. This could be rooted in past experiences of rejection, trauma, or insecurity. Moreover, societal norms and cultural influences may reinforce dismissive behaviors, promoting competition over collaboration or valuing certain perspectives over others.
In interpersonal relationships, dismissiveness can manifest in various forms. It may appear as overt disregard, where one belittles or ignores the contributions of others. Alternatively, dismissiveness can be subtle, expressed through nonverbal cues, such as eye-rolling or interrupting, that convey a lack of interest or respect. Regardless of its manifestation, dismissiveness undermines trust, erodes communication, and diminishes the sense of mutual regard essential for healthy relationships.
Effects of Dismissiveness:
The effects of dismissiveness ripple through both individual well-being and broader social dynamics. On a personal level, being on the receiving end of dismissive behavior can evoke feelings of inadequacy, frustration, or resentment. Over time, repeated experiences of dismissal may erode self-esteem and confidence, fostering a sense of isolation or alienation.
In professional settings, dismissiveness can impede collaboration and innovation. When team members feel their input is undervalued or dismissed, they may become disengaged or hesitant to contribute, stifling creativity and productivity. Moreover, dismissive leadership can create toxic work environments, where employees feel demoralized and unsupported, leading to high turnover rates and diminished organizational effectiveness.
In broader societal contexts, dismissiveness can exacerbate social inequalities and marginalization. When certain voices are routinely dismissed or invalidated, systemic injustices persist, hindering progress towards inclusivity and equality. Dismissive attitudes towards marginalized groups can perpetuate stereotypes, discrimination, and structural barriers to access and opportunity.
Overcoming Dismissiveness:
Addressing dismissiveness requires both individual reflection and collective action. At the personal level, cultivating empathy and self-awareness is essential. By acknowledging our own biases and insecurities, we can recognize when dismissive tendencies arise and actively work to counteract them. Practicing active listening, validating others’ experiences, and fostering open-mindedness are key steps towards building more respectful and inclusive relationships.
In professional settings, organizations can promote a culture of respect and collaboration through policies and practices that prioritize diversity, equity, and inclusion. Training programs that emphasize communication skills, conflict resolution, and unconscious bias awareness can help employees recognize and address dismissive behaviors. Additionally, leaders play a crucial role in modeling respectful and inclusive behavior, setting the tone for the entire organization.
On a societal level, challenging dismissive attitudes requires collective efforts to dismantle systemic barriers and promote social justice. This involves amplifying marginalized voices, advocating for policy reforms, and fostering dialogue and understanding across diverse perspectives. By valuing and affirming the dignity and worth of all individuals, we can create a more equitable and compassionate society.
Conclusion:
Dismissiveness is a pervasive yet often overlooked aspect of human interaction with far-reaching consequences. By understanding its underlying causes, acknowledging its effects, and committing to overcoming it, we can cultivate healthier relationships, more effective organizations, and a more just and inclusive society. Through empathy, respect, and collaboration, we can build a world where every voice is heard and valued.