Volume Calculator
Volume calculation, a fundamental concept in mathematics and engineering, plays a crucial role in various fields, ranging from construction and manufacturing to science and everyday life. Whether you’re determining the capacity of a container, estimating material quantities for a project, or analyzing the behavior of a substance, understanding how to calculate volume accurately is indispensable. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into the principles, methods, and practical applications of volume calculation, equipping you with the knowledge to tackle volume-related challenges with confidence.
Table of Contents
ToggleUnderstanding Volume:
Volume refers to the amount of space occupied by a three-dimensional object. It’s commonly measured in cubic units, such as cubic meters (m³) or cubic centimeters (cm³), depending on the scale of the object being measured. The concept of volume applies to various geometric shapes, including cubes, spheres, cylinders, cones, and irregular solids.
Basic Formulas for Volume Calculation:
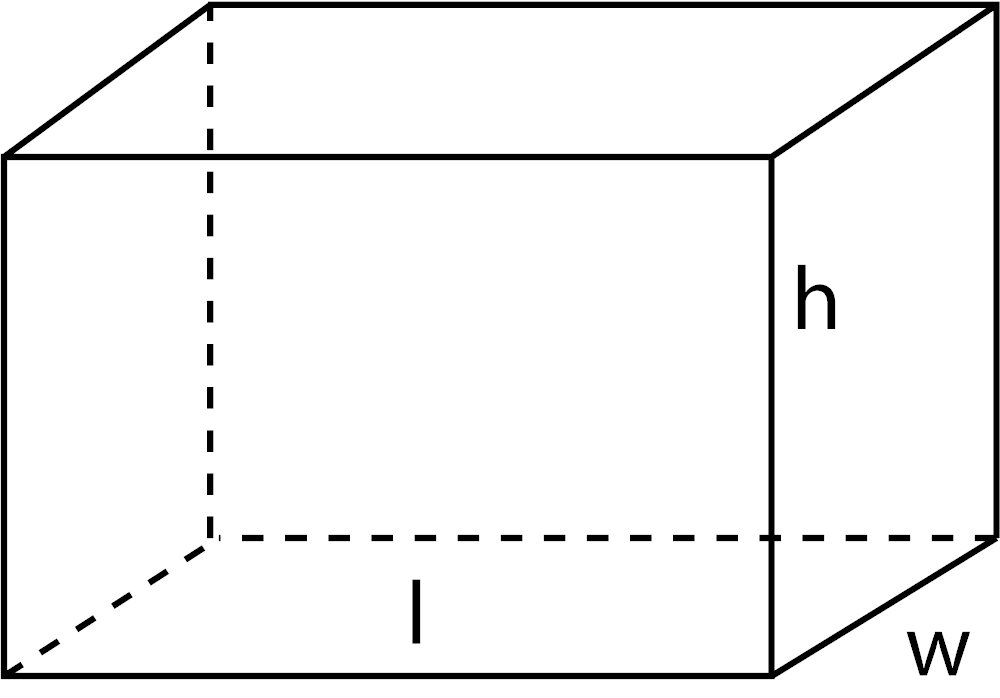
- Cubes and Rectangular Prisms: The volume of a cube or rectangular prism is calculated by multiplying the length, width, and height of the object: Volume = Length × Width × Height
- Cylinders: The volume of a cylinder is determined by multiplying the area of the base (πr², where r is the radius of the base) by the height of the cylinder: Volume = πr² × Height
- Spheres: The volume of a sphere is calculated using the formula: Volume = (4/3)πr³
- Cones: The volume of a cone is found by multiplying the area of the base by the height of the cone and dividing by 3: Volume = (1/3)πr² × Height
Practical Applications:
- Construction and Engineering: Volume calculation is essential in construction projects for determining the amount of materials needed, such as concrete, gravel, or soil. Engineers also rely on volume calculations for designing structures and analyzing fluid dynamics.
- Manufacturing and Production: In manufacturing processes, volume calculation is used to determine the capacity of containers, tanks, and reservoirs for storing liquids or gases. It’s also crucial for optimizing production efficiency and managing inventory levels.
- Scientific Research: Scientists use volume calculation extensively in various fields, including chemistry, physics, and biology. From measuring the volume of a solution in a laboratory experiment to analyzing the volume of a celestial body in astrophysics, accurate volume calculations are indispensable for advancing scientific knowledge.
- Architecture and Interior Design: Architects and interior designers utilize volume calculation to assess spatial requirements, plan room layouts, and estimate material quantities for construction and renovation projects. It helps them create functional and aesthetically pleasing spaces while adhering to budget constraints.
Advanced Techniques and Tools:
- Integration and Calculus: For irregular shapes or objects with varying cross-sectional areas, volume calculation may require advanced mathematical techniques such as integration. Calculus enables the determination of volume by summing infinitesimal volumes across the entire object.
- Computer-Aided Design (CAD) Software: CAD software applications offer sophisticated tools for generating three-dimensional models and performing accurate volume calculations. These tools are extensively used in architecture, engineering, and manufacturing industries for design optimization and simulation.
Challenges and Considerations:
- Accuracy and Precision: Achieving accurate volume calculations depends on the precision of measurements and the complexity of the object being analyzed. Small errors in measurements or assumptions can significantly impact the reliability of the results.
- Units and Conversions: It’s essential to maintain consistency in units when performing volume calculations. Converting between different unit systems, such as metric and imperial, requires attention to detail to avoid errors in the final calculations.
Conclusion:
Volume calculation is a fundamental skill with broad applications across various industries and disciplines. Whether you’re a student, a professional engineer, or an enthusiast, mastering the art of volume calculation empowers you to solve complex problems, optimize designs, and make informed decisions. By understanding the principles, formulas, and practical techniques outlined in this guide, you’ll be well-equipped to tackle volume-related challenges with confidence and precision. Embrace the versatility of volume calculation, and unlock new possibilities in your endeavors.





